General Characteristics of Compounds of the Alkaline Earth Metals
General Characteristics of Compounds of the Alkaline Earth Metals: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Compounds of Alkaline Earth Metals, Oxides of Alkaline Earth Metals, Hydrides of Alkaline Earth Metals & Carbide formation by alkaline earth metals etc.
Important Questions on General Characteristics of Compounds of the Alkaline Earth Metals
The solubilities of carbonates decrease down the magnesium group due to a decrease in
How magnesium bicarbonate is formed? Give some examples of bicarbonates of alkaline earth metals.
Compare the solubility of calcium bicarbonate and calcium carbonate in water.
Which of the following is soluble in water?
Which of the following is soluble in water?
is soluble in water because
Which of the following compounds is most soluble in water ?
Which are correct statements for and ?
Among the following, the compound that is readily soluble in water is
Which would you expect to have a higher melting point, magnesium oxide or magnesium fluoride? Explain your reasoning.
Which of the following oxides is most acidic in nature?
According to Fajan rules, the percentage covalent character in an ionic compound increases if the cation is highly charged or the cation is small and the anion is large or the cation has pseudo inert gas configuration. As a result of increased covalent character, the melting point decreases and solubility in less polar solvent increases.
The highest lattice energy corresponds to
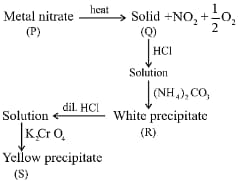
From the above sequence of reactions, identify P,Q,R and S
| P | Q | R | S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (i) | ||||
| (ii) | ||||
| (iii) | ||||
| (iv) |
Select the basic anhydride?
In the given orders, correct ones are:-
(I) Thermal stability
(II) Basic Nature
(III) Solubility in water
(IV) Melting point
Study the following reaction:
The metal carbide is-
An alkaline earth metal carbide undergoes hydrolysis to form . The metal carbide which can be used for this reaction is:
A metal readily forms water soluble sulphate , water insoluble hydroxide and oxide which becomes inert on heating. The hydroxide is soluble in . The metal is
The value of is maximum for:
Why does the solubility of alkaline earth metal carbonates and sulphates decrease down the group?
